Cygnus (constellation)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 | |
| List of stars in Cygnus | |
| Abbreviation: | Cyg |
| Genitive: | Cygni |
| Symbolism: | the Swan or The Northern Cross |
| Right ascension: | 20.62 h |
| Declination: | +42.03° |
| Area: | 804 sq. deg. (16th) |
| Main stars: | 9 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars: | 84 |
| Stars with known planets: | 6 |
| Bright stars: | 6 |
| Nearby stars: | 1 |
| Brightest star: | Deneb (α Cyg) (1.25m) |
| Nearest star: | 61 Cyg (11.4 ly) |
| Messier objects: | 2 |
| Meteor showers: | October Cygnids Kappa Cygnids |
| Bordering constellations: | Cepheus Draco Lyra Vulpecula Pegasus Lacerta |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −40° Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of September | |
Cygnus (pronounced /ˈsɪgnəs/) is a northern constellation. Its name is Latin for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 1st century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Notable features
[edit] Stars
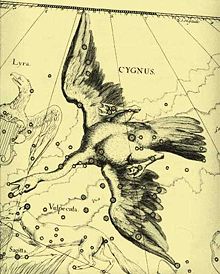
Albireo, a double star with blue and yellow components is at the "head". Deneb, its brightest star, is at the tail and is one star of the summer triangle.
[edit] Deep sky objects
Several star clusters and nebulae are found in Cygnus due to its position on the Milky Way. The North America Nebula (NGC 7000) is found a bit to the east of Deneb. Its resemblance to the continent is best appreciated in photographs. The Pelican Nebula (IC 5070) is nearby.
To the south of Epsilon Cygni is the Veil Nebula (NGC 6960, 6962, 6979, 6992, and 6995) which is an ancient supernova remnant covering approximately 3 degrees of the sky.
Also of note is the Crescent Nebula (NGC 6888), located between Gamma and Eta Cygni, which was formed by the Wolf-Rayet star HD 192163.
More supernovae have been seen in the Fireworks Galaxy (NGC 6946) than in any other galaxy.
The constellation also contains the X-ray source Cygnus X-1, which is now known to be caused by a black hole accreting matter in a binary star system. The system is located close to the star Eta Cygni on star charts.
[edit] History and mythology
The constellation can be represented as looking like a wide winged, long necked bird, in graceful flight [1]. In Greek mythology, it has been identified with several different legendary swans. Zeus disguised himself as a swan to seduce Leda, who gave birth to the Gemini, Helen of Troy, and Clytemnestra; Orpheus was transformed into a swan after his murder, and was said to have been placed in the sky next to his lyre (Lyra); and the King Cycnus was transformed into a swan.[citation needed]
In Ovid's Metamorphoses, there are three people named Cygnus, all of whom are transformed into swans. Alongside Cycnus, noted above, he mentions a boy from Tempe who commits suicide when Phyllius refuses to give him a tamed bull that he demands, but is transformed into a swan and flies away. He also mentions a son of Neptune who is an invulnerable warrior in the Trojan War who is eventually defeated by Achilles, but Neptune saves him by transforming him into a swan.
Cygnus, together with other constellations in the Zodiac sign of Sagittarius (specifically Lyra and Aquila, together with Sagittarius itself), may be a significant part of the origin of the myth of the Stymphalian Birds, one of The Twelve Labours of Heracles.[original research?]
In Chinese mythology, the constellation Cygnus is the site of the once-a-year magpie bridge (鹊桥, Que Qiao) which connects the lovers Niu Lang and Zhi Nu (see Qi Xi).
[edit] Musical references
Sonata Arctica's song "Fly With The Black Swan," The Mars Volta's song "Cygnus....Vismund Cygnus," and Rush's song "Cygnus X-1" are references to Cygnus.

No comments:
Post a Comment